Raghvendra Kumar Kushwaha
M.Sc. (Agri.) Soil Science
Sam Higginbottom University of Agriculture, Technology and Sciences
Allahabad-211007,U.P.
Soil fertility –
Soil fertility refers to the ability of soil to sustain agricultural plant growth, to provide plant habitat and result in sustained and consistent yields of high quality. Physical, chemical and biological power, all three have their own importance for the growth and development of plant. If even one power is less, then the fertility and health of the soil will be less. For example, the soil has enough nutrients for the growth of plants, but if the drainage is not proper, then due to lack of drainage, there will be a decrease in soil air, which will affect the growth of soil organisms, creating adverse conditions for them. Will have low fertility or health. The fertility or health of all productive land may be good, but the productivity of all fertile land may not be good. This can happen due to lack of water drainage in the land. due to adverse climatic conditions.
A healthy soil has the ensuing characteristics
1. The ability to supply essential nutrients and water in adequate amounts and proportions for plant growth and reproduction.
2. The absence of toxic substances which may inhibit plant growth.
Soil fertility provides a favorable environment for plant growth. It refers to the ability of the soil fertility and crop production while reducing environmental impact.
Definition-
“The status of a soil with respect to its ability to supply elements essential for plant growth without a toxic concentration of any element”
Foth & Ellis (1997)
Or
“Soil fertility refers to the ability of the soil to sustain plant growth”
Or
“Soil fertility is the ability of a soil to sustain plant growth by providing essential plant nutrients and favorable chemical, physical, and biological characteristic as a habitat foe plant growth”
14 nutrients are supplied to plant through fertilizers and soil, and 17 essential nutrients, including C,H,O(which plants get from air and water),are needed to sustain soil fertility. The table below describes the essential and beneficial nutrients derived from the soil.
| Nutrient family | Nutrient | Symbol | Availability Percentage of plant | Major function in plant |
| Primary | Nitrogen | N | 1.75 | Chlorophyll, cell formation |
| Phosphors | P | 0.25 | Protein syntheses, fat and carbohydrate metabolism | |
| Potassium | K | 1.5 | Water regulation, enzyme activity | |
| Carbon | C | 45 | Plant structures | |
| Oxygen | O | 45 | Respiration, energy production | |
| Hydrogen | H | 6.0 | Synthesis of carbohydrates, water retention | |
| Secondary | Calcium | Ca | 0.05 | Root permeability |
| Magnesium | Mg | 0.20 | Chlorophyll, fat formation and metabolism | |
| Sulfur | S | 0.03 | Vitamin and oil formation | |
| Micro | Chlorine | Cl | 0.01 | Enzyme activity, cellular development |
| Iron | Fe | 0.01 | Enzyme development and activity | |
| Zinc | Zn | 0.002 | Enzyme activity | |
| Manganese | Mn | 0.005 | Pigmentation, Enzyme activity | |
| Boron | B | 0.0001 | Enzyme activity | |
| Copper | Cu | 0.0001 | Enzyme activity | |
| Molybdenum | Mo | 0.00001 | Nitrogen fixation in legumes |
Factors affecting Soil fertility- Two categories can be made of the variables influencing soil fertility.
1. Natural Factors
2. Artificial Factors
1. Natural Factors- These factors affect the soil structure and their effect
starts from the time of soil formation.
a) Parent Material
b) Climate
c) Soil Age
d) Topography
e) Physical Condition of Soil
f) Soil Erosion
2. Artificial Factors- These factors are related to soil management
a) Use of Manures and Fertilizers
b) Weeds Control
c) System of Growing Crop
d) Water Logging
e) Method and time of Plowing the Soil
Soil Fertility management by organic farming-
Maintenance of soil fertility is one of the major benefits of organic farming systems. There are many concerns of managing soil fertility under organic farming system. Soil organic carbon is playing an important role in maintaining soil fertility. Soil health and quality is the foundation of organic farming and therefore maintenance of soil biological status is one of the important components in organic soil. Due to the different nutrient management practices in organic farming compared to abundance. Diversity and its activities in organic soils are expected to be significantly different from those in conventional soils. In addition, other crop management practices also affect soil microbial activities and thus improve soil health and organic farming is a production system that excludes the use of artificially compounded fertilizers, pesticides, growth regulators, geneticaiiy modified organism, antibiotics and livestock feed additives.
Soil fertility management by organic farming can be improved by using the following types of methods-
1) Vermicompost
2) Green Manures
3) Farmyard Manure
4) Crop rotation
5) Bio- fertilizer
1) Vermicompost- Vermicompost makes a special contribution to soil fertility management through organic farming. Vermicomposting can improve soil structure and soil fertility by increasing porosity and aeration, and improving soil moisture- retention, all of which help increase crop yield. Can do. Adding vermi compost the soil can increase the activity of micro-organisms 20 times more than that of the soil itself and there by improving soil structure and promoting healthy, fertile soil.
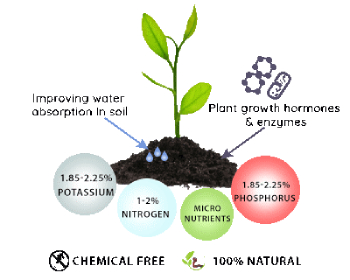
2) Green Manure- Adding green manure to the soil improves its physical condition by increasing the amount of organic matter in the field.
- The following types of benefits are obtained by using green manure in the soil-
- Improves the soil structure
- Provision of nutrients and organic carbon of soil
- Prevention of erosion
- Improving aeration in rice soils by stimulating activities of surface film of algae and bacteria
- Preventing leaching of soluble nutrients from the soil
- Increases the water holding capacity of light soil
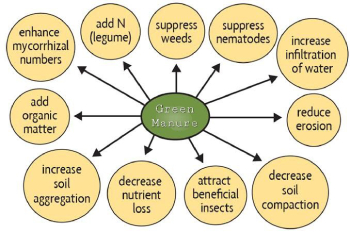
Fig- The Following benefits are obtained by mixing green manure in the soil
3) Farmyard Manure - In soil fertility management by organic farming , green manure crop are highly beneficial for the soil. they are widely used for upgrading soil, weed control, nutrients and various organic matter and also increase soil fertility. And in general improves the condition of the soil and application of dung manure in soil reduces bulk density and compaction in soil and also increases overall stability, water infiltration and retention of soil.
4) Crop rotation- Soil fertility management through organic farming helps in returning nutrients to the soil in crop rotation without synthetic inputs. The practice also serves to disrupt pest and disease cycles, improve soil health by increasing biomass from the root structures of various crops, and increase on- farm biodiversity.
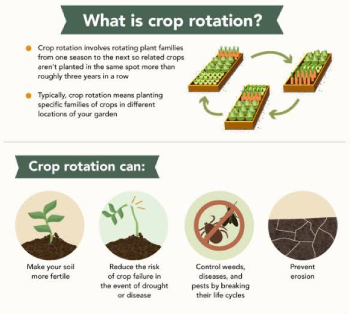
Fig- By using crop rotation in the soil.
5) Bio- fertilizer- Bio-fertilizer is a fertilizer made from living micro-organisms. When applied in the field, it promotes plant growth by increasing the supply or availability of primary nutrients to the host plant. This helps in increasing the fertility of the soil. Cyanobacteria autotrophic microbes, e.g., Anabaena, Nostoc, Oscillatoria can fix atmospheric nitrogen in an aquatic and terrestrial environment and also add organic matter to the soil and increase its fertility.
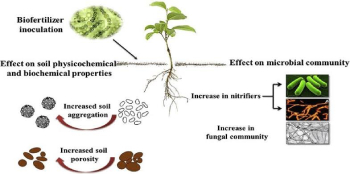
Fig- By using bio-fertilizer in the soil.
Benefits of Soil Fertility management by organic farming- The following types of benefits are obtained from improving soil fertility through organic farming which are as follows.
a) It improves the soil’s chemical properties such as supply and retention of soil nutrients, reduces nutrient loss into water bodies and environment and promotes favorable chemical reactions.
b) It improves the soil physical properties such as granulation, good tilth, good aeration, easy root penetration and improves water-holding capacity and reduces erosion.
c) It reduces the cost of agricultural production and also improves the soil health.
d) Manures are a useful way of transferring nutrients (and fertility) around the farm.
e) Improving aeration in rice soils by stimulating activities of surface film of algae and bacteria.
f) Provision of nutrients and organic carbon of soil.







